At a glance: The U.S. National Biotechnology and Biomanufacturing Initiative (NBBI)
Mid-September 2022, President Biden signed an executive order (EO) to launch a U.S. National Biotechnology and Biomanufacturing Initiative (NBBI). The NBBI aims to ensure strengthened U.S. supply chains and to drive the U.S. bioeconomy, which is valued currently at nearly one trillion dollars, towards an anticipated global value of $30 trillion in the next two decades. To reach this goal, the President has commissioned main governmental agencies to provide reports on the opportunities, challenges, and risks of biotechnology, which will be made available earliest end of the year.
A total of $2B associated funding was earmarked for the NBBI, leveraging U.S.-based biomanufacturing, advancing biotechnology development, and accelerating research on bioproducts and biomaterials. This funding follows the recently issued CHIPS and Science Act, which authorized a total $280B investment into technological progress.
President Biden commissioned main U.S. federal agencies to investigate key opportunities and challenges of emerging biotechnology
An executive order commissions federal agencies to take actions, in this case the departments of energy, defense, health, and commerce, and the U.S. department of agriculture (USDA). Departments are required to provide reports investigating key opportunities, challenges and risks associated with biotechnology. Earliest reports will be made publicly available 90 days after the EO’s release, in December 2022. Even though we do not know the specific contents yet, we know that the reports will provide new insights through:
- a review of the current regulatory framework provided by the USDA, following up on EO 13874 issued in 2019, which identified regulatory requirements for bio-manufactured products.
- detailed assessments of agencies on key challenges and uncertainties, including how biobased products can be used to tackle climate change, and how biotechnology can be applied to advance a sustainable food system.
- a bioeconomy lexicon, describing and evaluating the whole U.S. bioeconomy landscape, which will be a valuable tool for companies, investors, and non-profit-organisations.
Through the NBBI, over $2B is invested in biotechnology: A push for the American bioeconomy
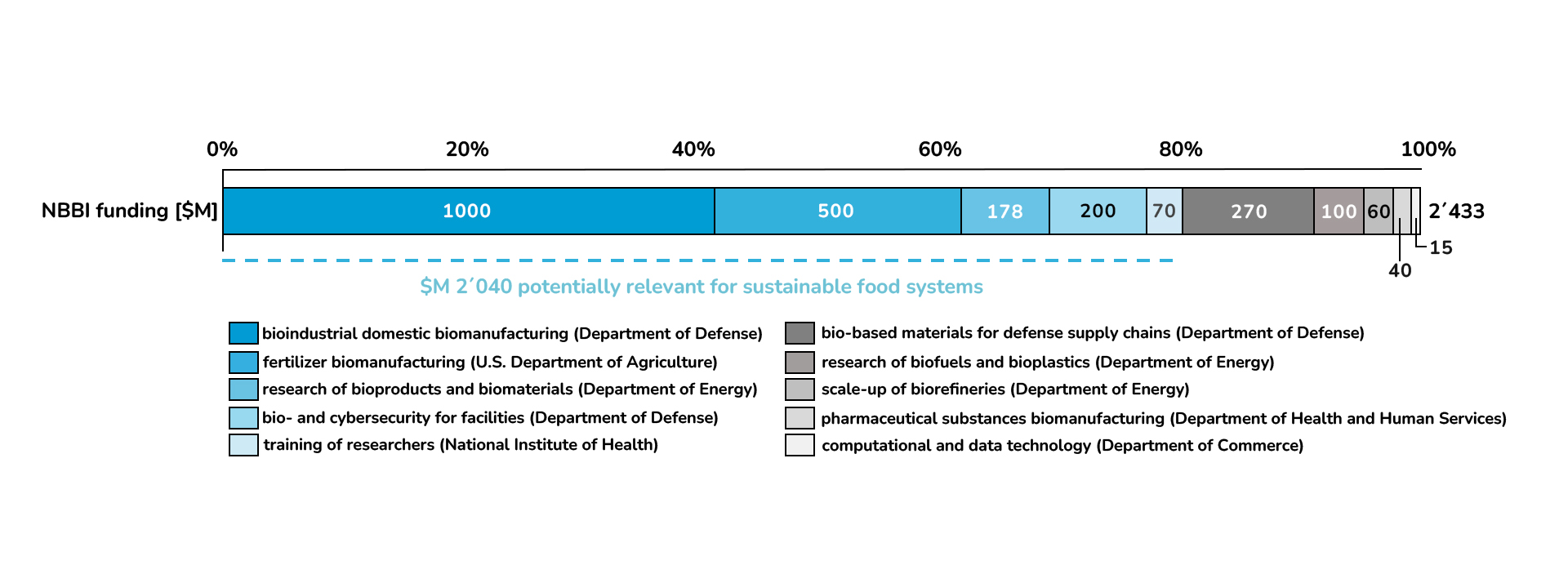
Through its associated funding package of over $2B, the NBBI frames a clear plan to action. The funding will ensure execution of the crucial steps defined in the agencies’ reports, with the biggest parts (Figure 1) leveraging the U.S. biomanufacturing, advancing fertilizer development, and research on bioproducts and biomaterials.
The NBBI further supports research initiatives to train future researchers, and thus indirectly contribute to the bioeconomy, as well as biomanufacturing of advanced pharmaceuticals or defence-related materials.
In addition to providing funding, the NBBI outlines measures to support production and sales, for example through preferred procurement of bioproducts. It thus builds on recent efforts to coordinate the roles of the main federal agencies and support the commercialisation of bioproducts.
Our perspective: The NBBI contributes towards the sustainable food system of the future
We at Blue Horizon see the NBBI as a strong signal that the U.S. government accelerates its efforts to create a flourishing bioeconomy, which will provide key building blocks for a sustainable and resilient food system. Advancing key technologies that enable the production of cheese, dairy or meat alternatives using, for instance, fermentation, can provide alternatives to mass animal agriculture, and limit associated environmental destruction.
‘The NBBI will act as a market stimulus for U.S. bioproducts, through creation of much needed domestic biomanufacturing capacity that can be used to produce a new generation of animal-free protein and lipid ingredients, and support for an accelerated and clear path to market for bioproducts’ says Nate Crosser, Principal at Blue Horizon, who is an expert on alternative proteins and has published leading industry reports for the Good Food Institute. ‘It will further help train the next generation of workers and stimulate sustainable government procurement. And perhaps most importantly, this is a strong signal that the world’s largest economy is serious about the transition from a petro- and animal economy to a bioeconomy.’
The NBBI-associated funding has the potential to advance the full supply chain of a sustainable food system
The sustainable food system may be a core beneficiary of the NBBI-associated funding, with around 80% of the total funding volume spent being potentially relevant to the food sector (Figure 1). The commitments cover the entire food value chain: From production of inputs (e.g., development of new crop seeds, biomanufacturing of fertilisers) to production of food ingredients (e.g., those enabled by fermentation like heme, which provides colour, taste, and nutritional benefits in alternative meats), to packaging (e.g., bioplastics) and distribution (e.g., biofuel), to recycling and waste management.
Although not explicitly mentioned, another emerging technology, the cell-based production of cultivated meat, may benefit from the initiative. A senior administration official stated during the press brief that ‘[The government is] also looking to improve food security and drive agricultural innovation, including through new technologies that [produce] foods made with cultured animal cells.’
The beneficiaries of the NBBI funding have not been defined, and specifics of funded projects have not been released yet. Detailed information is expected to be available following the publication of commissioned governmental reports mid-December 2022. Exciting times for sustainable food!